Analysis of the Genoa Bridge Collapse: Causes of the Disaster 🇮🇹🔍 #Genoa #Italy #Engineering

Genoa Bridge Collapse: Causes & Analysis
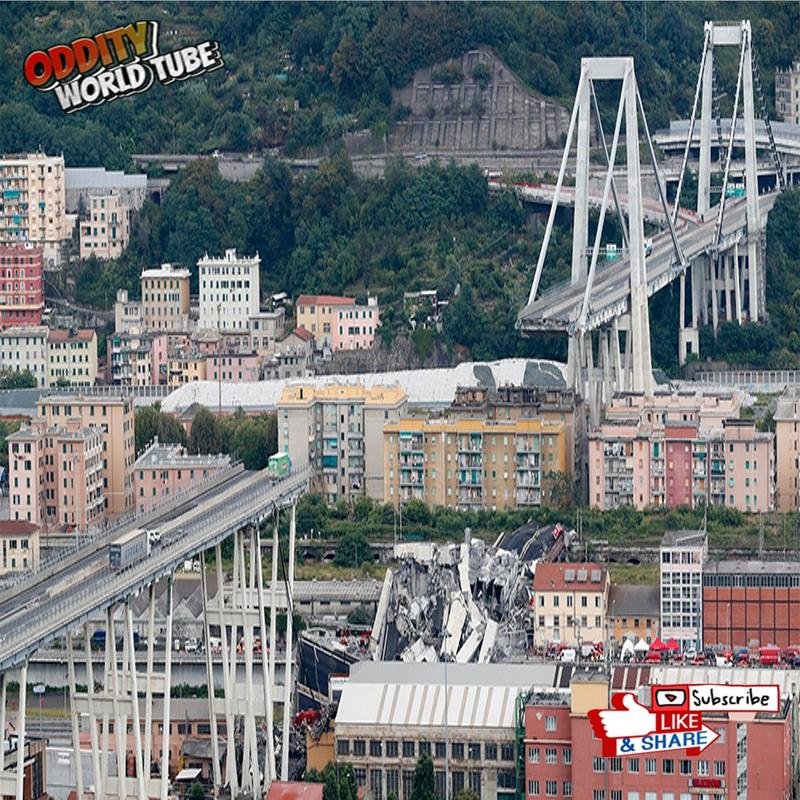
On August 14, 2018, the catastrophic collapse of a significant section of the Morandi Bridge (also known as the Polcevera Bridge) in Genoa, Italy, shocked the world. This disaster, resulting in numerous fatalities and the destruction of vehicles, exposed critical engineering and managerial deficiencies, raising global concerns regarding infrastructure safety.
The Disaster
Designed by Riccardo Morandi and inaugurated in 1967, the Morandi Bridge was a vital component of the A10 motorway connecting Italy and France. Its innovative cable-stayed reinforced concrete design, while groundbreaking at the time, ultimately proved susceptible to deterioration. The collapse occurred amidst severe weather conditions, including heavy rain and strong winds. The event was devastating; approximately 210 meters of the bridge plummeted, sending vehicles falling approximately 45 meters. The incident resulted in 43 fatalities, numerous injuries, and the displacement of hundreds of residents. Intensive search and rescue operations immediately commenced, with emergency services working tirelessly to locate survivors and recover victims.
Causes and Investigations
Preliminary investigations attributed the collapse to several factors, primarily the deterioration of the reinforced concrete and supporting cables. Despite years of repairs and maintenance, the bridge’s structural problems proved insurmountable. Experts also identified design flaws, specifically the reliance on a relatively small number of cables to support substantial bridge sections. Subsequently, the Italian government launched a comprehensive investigation to determine liability. Numerous officials and engineers responsible for bridge maintenance faced charges of manslaughter and gross negligence. Furthermore, companies operating the A10 motorway underwent scrutiny to ensure compliance with safety and maintenance regulations. The collapse ignited widespread debate concerning the role of private entities in managing public infrastructure and whether profit maximization compromised safety.
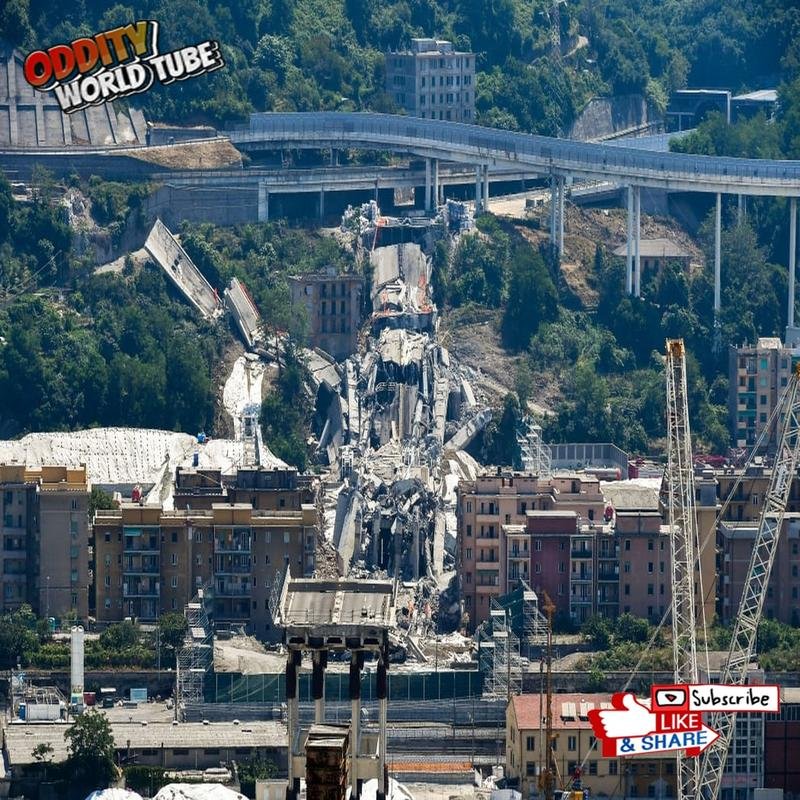
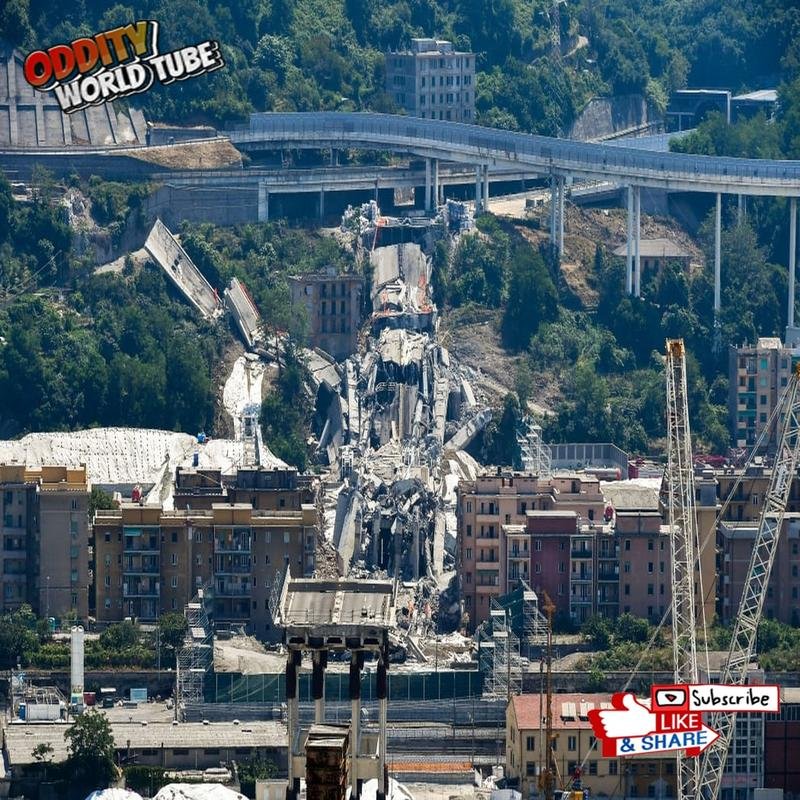
Aftermath and Reconstruction
The subsequent debris removal was a massive and complex undertaking, requiring heavy machinery to clear the scattered concrete and steel. This included the demolition of damaged nearby structures and the provision of alternative housing for displaced residents. The process, spanning several months, implemented stringent safety protocols for both workers and the public. Following debris removal, construction of a replacement bridge, designed by Renzo Piano, commenced. Completed at an expedited pace, the Genoa San Giorgio Bridge opened in August 2020, symbolizing hope and renewal for Genoa.
Impact and Lessons Learned
The Morandi Bridge collapse significantly impacted Genoa and the Italian economy, disrupting traffic, trade, and tourism. It underscored the critical importance of infrastructure maintenance and spurred calls for increased investment. The Italian government pledged billions of euros towards nationwide infrastructure modernization, encompassing roads, bridges, and tunnels. Moreover, the collapse prompted critical examination of oversight and regulatory roles in ensuring infrastructure safety, with the Italian government and private companies facing criticism for inadequate preventative measures. Advocates called for enhanced infrastructure oversight, stricter penalties for negligence, and increased accountability.
The collapse served as a stark warning, prompting immediate global action to enhance infrastructure safety. A human tragedy, it exposed vulnerabilities in infrastructure management and serves as a constant reminder of the paramount importance of safety, maintenance, and investment in infrastructure. We must learn from this tragedy and collaborate to prevent future incidents. The Genoa incident remains a potent symbol of both loss and hope, a catalyst for change and improvement. The Morandi Bridge collapse transcends a simple structural failure; it reflects deeper societal challenges, underscoring the importance of accountability, transparency, and prioritizing safety in all decisions. This event should inspire collective action towards building a safer and more sustainable future.