The Neuroscience of Romantic Attraction
Romantic Love: Brain Chemistry & Neural Mechanisms
Romantic love profoundly impacts our brain chemistry, triggering a complex cascade of neurobiological processes. Understanding these processes offers fascinating insights into the intense emotions and behaviors associated with romantic attraction.
The Chemistry of Love
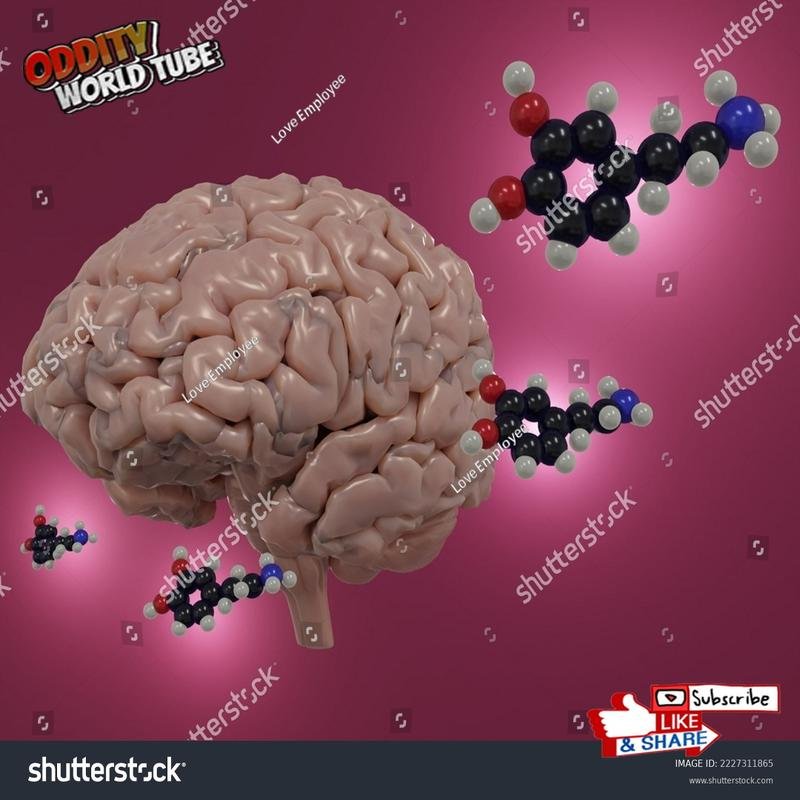
The initiation of romantic love elicits the release of phenylethylamine, an endogenous amphetamine-like compound, leading to increased arousal and excitement. This surge of phenylethylamine contributes to the euphoric feelings and heightened energy often experienced in the early stages of a relationship.
The Role of Dopamine
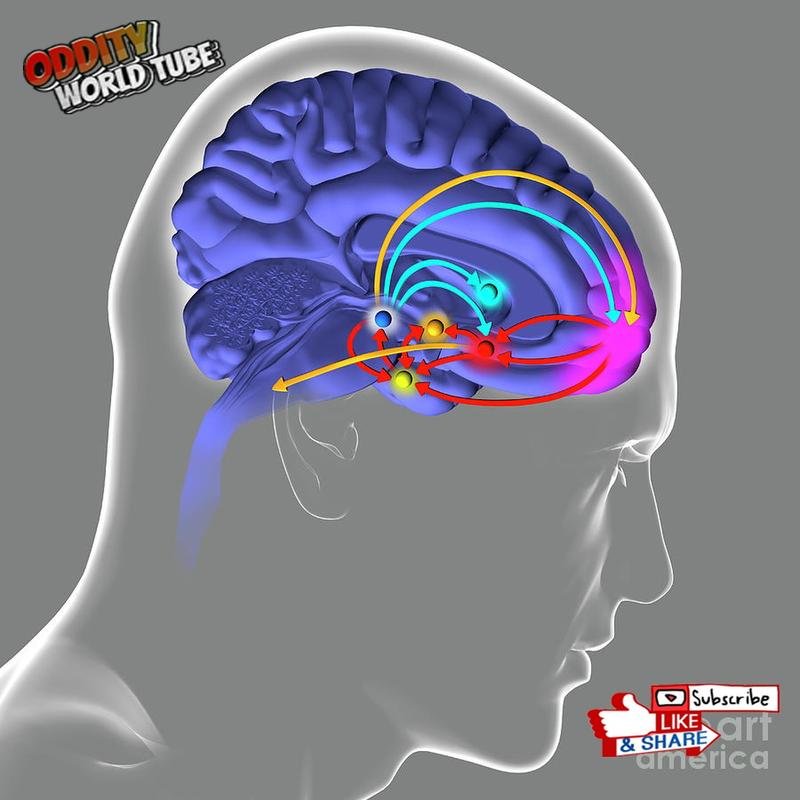
Concurrently, dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with reward processing, exhibits heightened activity within the brain’s ventral tegmental area—a region also implicated in the effects of addictive substances. This dopaminergic surge underlies the intense pleasure and craving often observed in the early phases of romantic relationships. The reward system activation reinforces the desire for connection and intimacy.
Neuroscientific Research
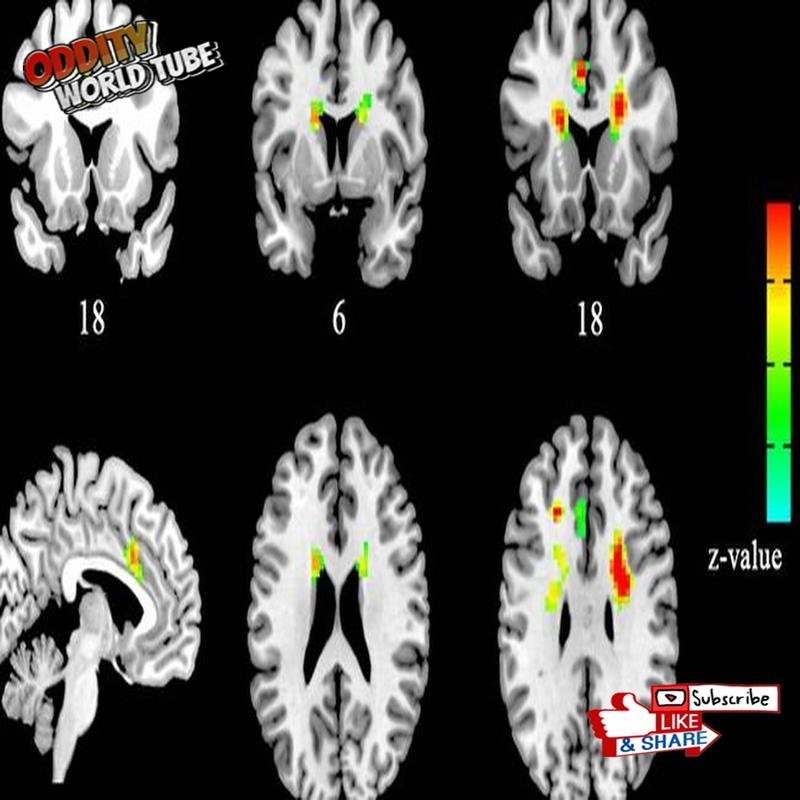
A 2005 University College London study demonstrated that activity in the anterior cingulate… [Further details on the UCL study could be added here]
Conclusion
The experience of romantic love is far more than just an emotional state; it’s a complex interplay of neurochemicals and brain regions working in concert. Further research continues to unravel the intricate neural mechanisms underlying this fundamental human experience.