Rapid Decision-Making: A Neuroscientific Perspective on Intuitive Judgments
Rapid Decision-Making: Brain & Intuition
Making decisions under pressure involves intricate neurological processes. This article explores the key brain regions and their interplay in enabling rapid, intuitive judgments.
The Role of the Amygdala
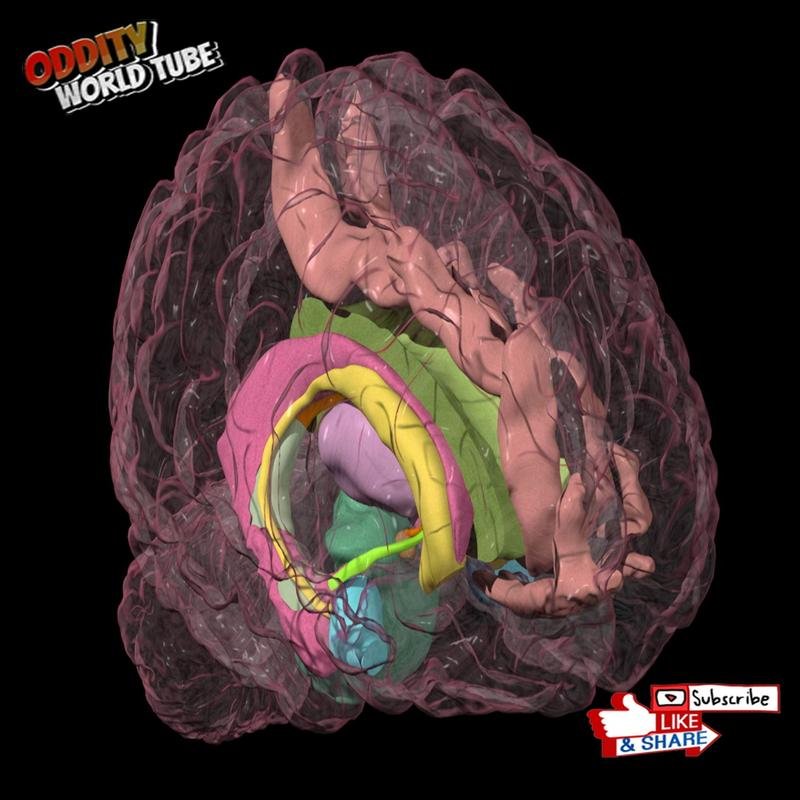
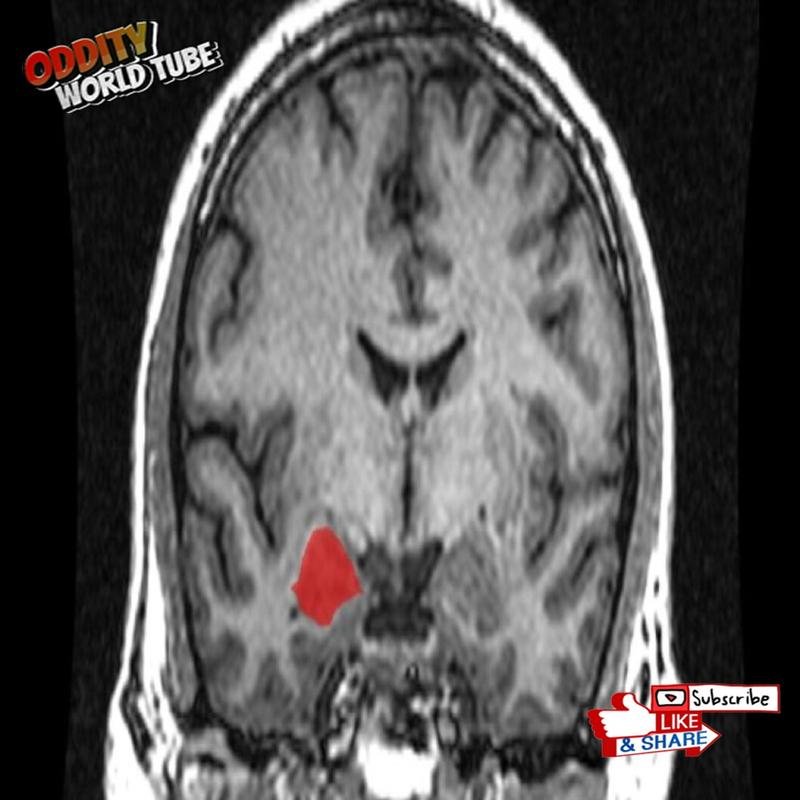
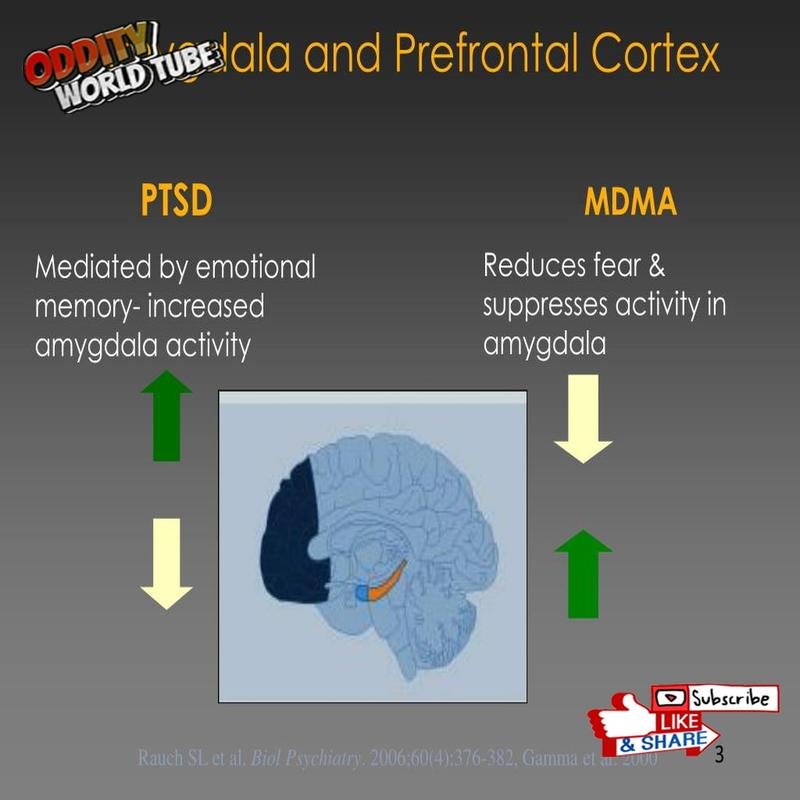
The amygdala, the brain’s emotional processing center, plays a pivotal role in rapid decision-making. Research from the University of Iowa in 1990 demonstrated that amygdala damage significantly impairs the rapid emotional processing crucial for expeditious decisions.
Prefrontal Cortex Interaction
The prefrontal cortex, responsible for cognitive functions, works dynamically with the amygdala. Neuroimaging studies, including a 2007 publication in *Science*, highlight increased activity in both regions during immediate decision-making, showcasing their collaborative role in swift judgments.
Conclusion
Understanding the interplay between the amygdala and prefrontal cortex provides crucial insights into the neurobiological mechanisms underlying rapid decision-making. This complex interaction allows us to make quick, often intuitive judgments, even under significant time constraints.