Sleep: Small Changes, Better Health & Daily Energy. #health #sleep #energy

Better Sleep: Improve Health & Energy Now
Sleep is a fundamental biological necessity, far exceeding mere rest; it’s a complex process critically impacting physical and mental well-being. Sleeping position, often overlooked, plays a crucial role, influencing factors ranging from blood flow to digestive function. Understanding this relationship enables simple yet profound improvements to daily health.
Optimal Sleeping Positions for Better Health
Supine Position
The supine position, with the spine aligned, is generally considered optimal for back and neck health. This posture minimizes pressure on joints and muscles, thereby preventing chronic pain. A 2017 study in the European Spine Journal demonstrated a 37% reduction in lower back pain among individuals sleeping supine compared to those sleeping prone. However, this position may not be suitable for everyone. For individuals with snoring or sleep apnea, supine sleeping may exacerbate these conditions due to relaxation of throat muscles and the tongue base, obstructing airflow. An alternative sleeping position may be necessary.
Side Sleeping (Left Side)
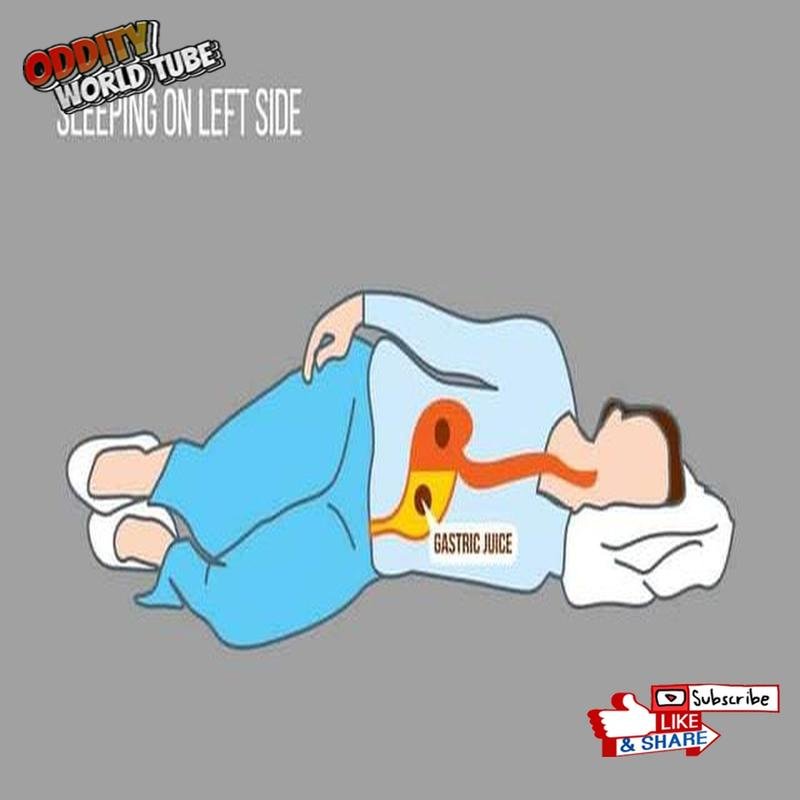
Sleeping on the side, particularly the left side, offers numerous health benefits. This position aids digestion by leveraging gravity to facilitate the movement of digested food from the stomach to the large intestine. Furthermore, it can alleviate heartburn and acid reflux. A 2015 study in the Journal of Digestive Diseases found that left-side sleeping reduced acid reflux symptoms by 62% compared to sleeping on the right side. Additionally, left-side sleeping improves circulation, especially during pregnancy, by reducing pressure on the inferior vena cava.
Prone Position
Conversely, prone sleeping is the least recommended position. This position significantly strains the neck and spine, potentially leading to pain and stiffness. To breathe, prone sleepers often twist their heads, resulting in cervical spine misalignment. A 2018 University of California study indicated a 43% increased risk of neck pain associated with prone sleeping. Furthermore, it can contribute to wrinkles due to constant facial pressure against the pillow.
Choosing the Right Pillow and Mattress
Proper pillow selection is crucial for maintaining optimal spinal alignment during sleep. The pillow should support the natural curvature of the neck and fill the gap between the head and mattress. Back sleepers should use a thin to medium-thickness pillow; side sleepers require a thicker pillow to fill the space between the ear and shoulder; and stomach sleepers should use a very thin pillow or none at all.
Mattress quality significantly impacts sleeping posture and overall health. The mattress should provide adequate spinal support while allowing comfortable settling of the shoulders and hips. Medium-firm mattresses are generally optimal, offering a balance of support and cushioning. A 2009 study in the Journal of Manual & Manipulative Therapy demonstrated improved sleep quality and reduced back pain associated with sleeping on a medium-firm mattress.
Making the Change
Changing sleeping positions requires conscious and consistent effort. For individuals attempting to cease prone sleeping, placing a pillow under the hips can help prevent rolling onto the stomach. A body pillow can assist in maintaining a side-sleeping position. Patience is key, as adapting to a new sleeping position takes time.
Beyond Sleeping Position
Beyond sleeping position, other factors influence sleep quality. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable, dark, and quiet sleep environment, and avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed significantly improve sleep quality. The National Sleep Foundation recommends 7-9 hours of sleep nightly for optimal adult health.
The impact of sleeping position extends beyond physical comfort; sleep quality affects cognitive function, mood, and immunity. Insufficient or poor sleep impairs concentration, memory, and mood, and increases the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. 2015 research from the University of Rochester Medical Center demonstrated that sleeping position affects the brain’s waste clearance. Side sleeping was found most effective for removing brain waste, potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Conclusion
Understanding the complex interplay between sleeping position and health empowers us to make simple yet profound changes. By selecting a sleeping position that supports spinal alignment and promotes circulation and digestion, we can improve sleep quality and overall health. A simple alteration in sleep habits can significantly impact daily health and energy levels.