The İzmit Earthquake: A Turkish Catastrophe – Shocking Facts

1999 İzmit Earthquake: Turkey’s Devastating Quake
The 1999 İzmit earthquake stands as a devastating natural disaster that exposed the vulnerability of Turkey’s infrastructure and underscored the critical need for robust disaster preparedness. This catastrophic event profoundly impacted Turkish society, prompting significant revisions to building codes and disaster response protocols.
The Earthquake’s Impact
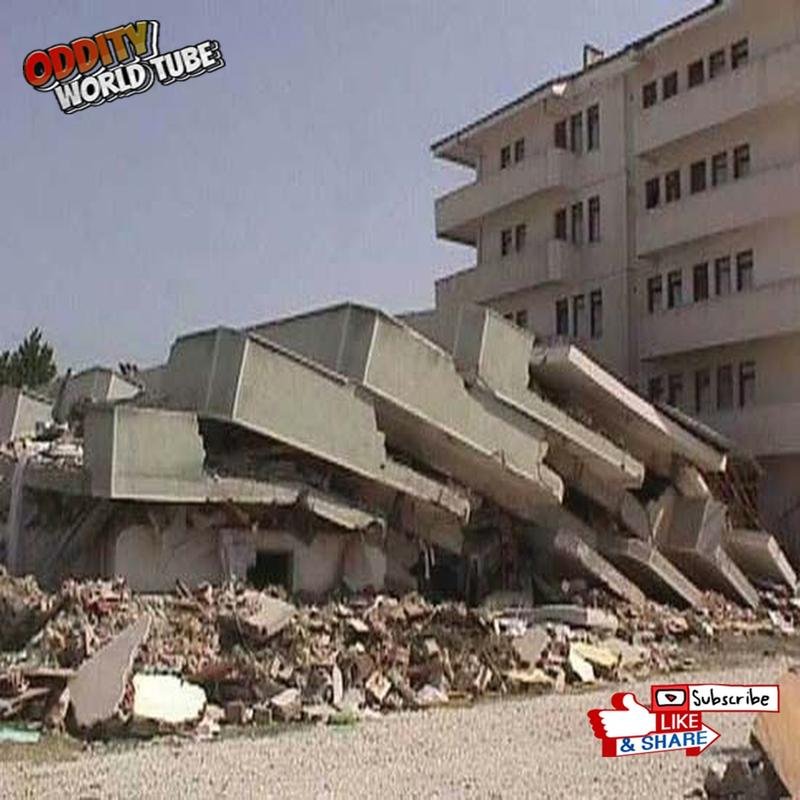
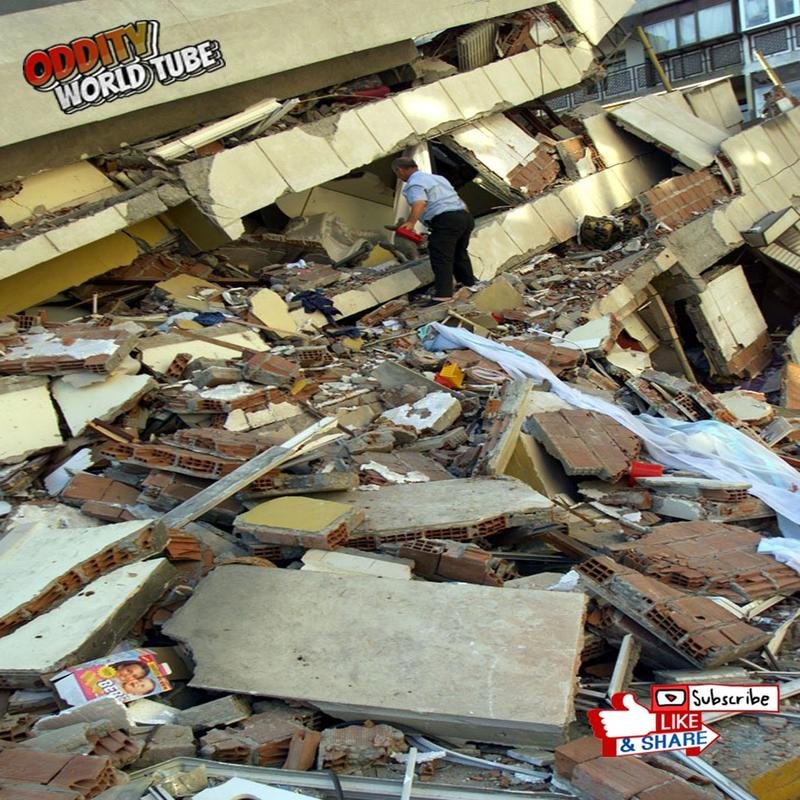
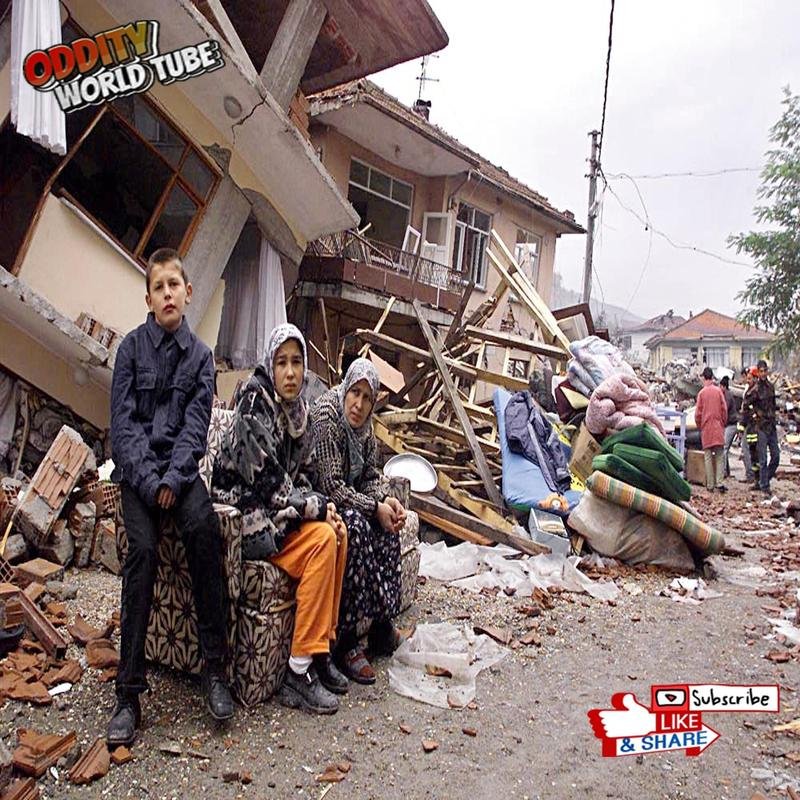
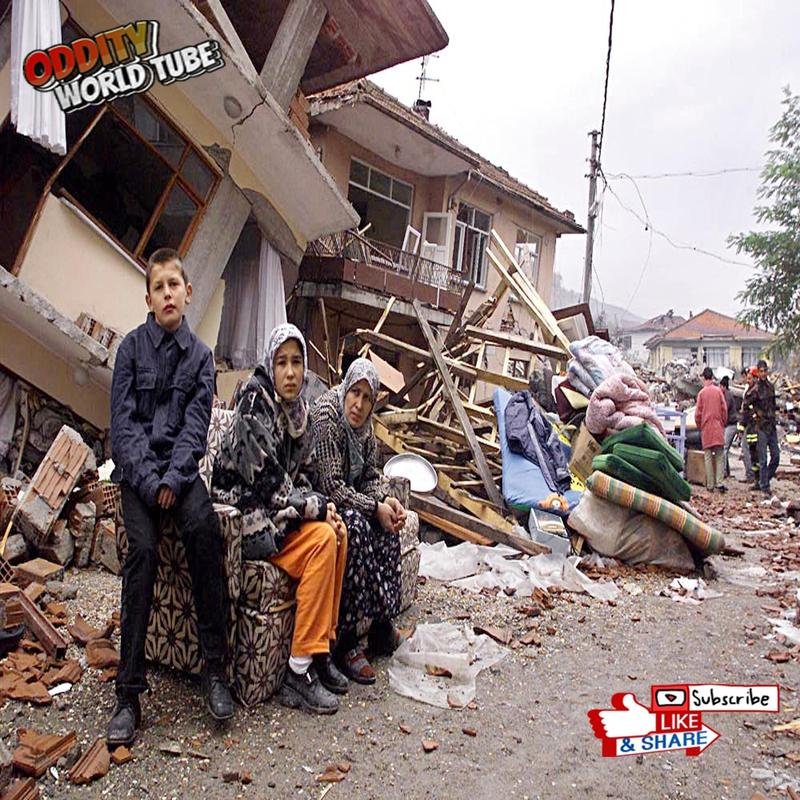
On August 17, 1999, at 03:02 local time, a powerful 7.6 magnitude earthquake (Richter scale) struck the İzmit region, lasting 37 seconds—a duration sufficient to cause widespread destruction. The epicenter’s proximity to Gölcük, a major naval base, exacerbated the losses. The earthquake resulted from a rupture along the seismically active North Anatolian Fault. The official death toll exceeded 17,000, while unofficial estimates suggest a figure potentially exceeding 45,000. Over 50,000 individuals sustained injuries, and hundreds of thousands were displaced. More than 250,000 buildings were damaged or destroyed, leaving a vast population homeless. The earthquake’s impact extended significantly to broader regions, including Istanbul and Ankara.
Causes of Catastrophic Losses
The catastrophic losses stemmed primarily from substandard construction and widespread non-compliance with building codes. Many structures utilized cheap, inferior materials and demonstrated poor workmanship, rendering them susceptible to collapse even in moderately strong seismic events. Furthermore, pervasive corruption facilitated the issuance of building permits without adequate structural safety checks. The initial disaster response was slow and inadequate, with the Turkish government struggling to effectively coordinate relief efforts and provide timely assistance to affected populations. Delays in the arrival of rescue teams and medical aid compounded the victims’ suffering. International non-governmental organizations played a vital role in providing humanitarian assistance.
Post-Earthquake Reforms
Following the İzmit earthquake, Turkey implemented significant changes to its building codes and disaster response mechanisms. Building regulations were strengthened to mandate the use of high-quality materials and rigorous construction procedures. The Disaster and Emergency Management Presidency (AFAD) was established to enhance the coordination of relief efforts and disaster response. Subsequent studies revealed that soft soil conditions in certain areas amplified the earthquake’s effects. Soil liquefaction, resulting in the loss of soil strength and stiffness, contributed to building collapses. Comprehensive soil studies were subsequently undertaken to assess seismic hazards and identify vulnerable areas.
Economic and Social Consequences
The İzmit earthquake had profound economic and social consequences, resulting in billions of dollars in economic losses and significantly impacting the nation’s economic growth. Many individuals lost their jobs and livelihoods, leading to increased poverty and unemployment. Survivors experienced severe psychological trauma, necessitating the provision of extensive psychological support services. The disaster also heightened awareness of the importance of earthquake insurance. Prior to the earthquake, earthquake insurance penetration was low; however, demand increased dramatically afterward. The government recognized the need to promote a culture of insurance to mitigate the financial burdens associated with future disasters.
Accountability and Transparency
Investigations revealed widespread corrupt practices involving numerous contractors and government officials, leading to the construction of unsafe buildings. Numerous individuals faced arrest and prosecution on charges of negligence and corruption. This issue sparked widespread public debate regarding accountability and transparency within the construction sector.
Conclusion
Despite efforts to enhance disaster preparedness, Turkey remains vulnerable to earthquakes due to its location on active seismic fault lines. Continued strengthening of building codes and improvements to disaster response practices are essential to minimize future loss of life and property. The anniversary of the İzmit earthquake serves as a stark reminder of the paramount importance of disaster preparedness and the adoption of necessary precautions to protect individuals and communities. Collaborative efforts between individuals and organizations are crucial in building more resilient communities capable of withstanding natural disasters. The İzmit earthquake remains a poignant lesson in the critical importance of structural safety, accountability, and transparency, representing a watershed moment in Turkish history that underscores the urgent need for improved infrastructure and disaster preparedness. This event should serve as a persistent reminder of the imperative to protect lives and property through effective preventative measures.