Why do the seasons change? 🌍 Science reveals the secret! 💡 #FourSeasons #Astronomy
Seasons: A Scientific Explanation of Earth’s Tilt
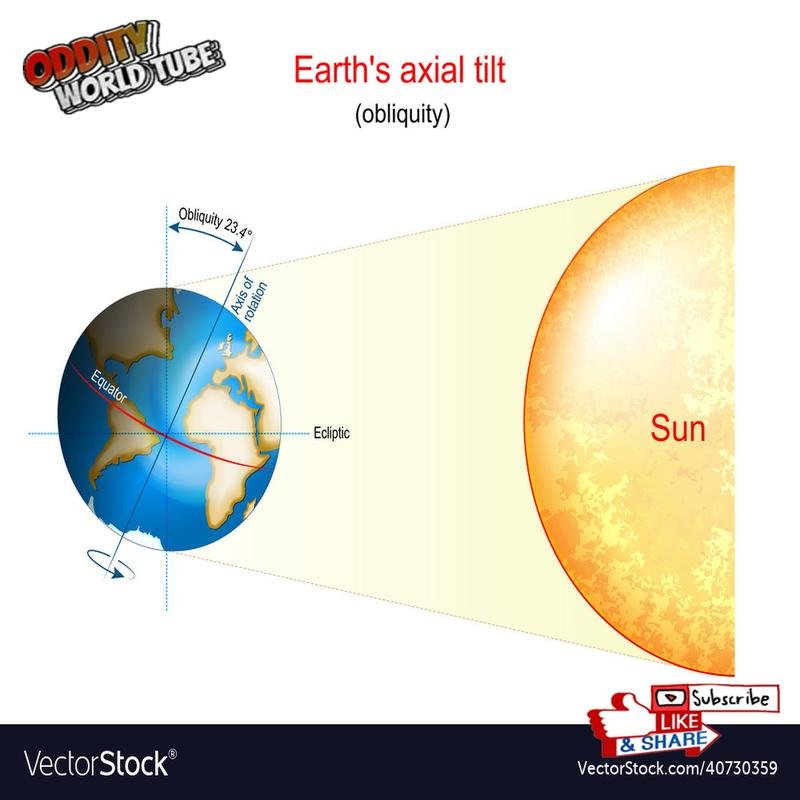
Seasonal variations are a fascinating consequence of Earth’s journey around the Sun. This isn’t simply a matter of distance; the key lies in Earth’s axial tilt.
Earth’s Tilt: The Driving Force
Earth’s axis is tilted at approximately 23.5 degrees. This tilt is the primary reason for the varying seasons we experience. As Earth orbits the Sun, different hemispheres receive varying amounts of direct sunlight, leading to changes in temperature and daylight hours.
Differential Solar Irradiance
The 23.5-degree tilt results in differential solar irradiance across the hemispheres. This means that the amount of solar energy received per unit area varies throughout the year. During the Northern Hemisphere’s summer (approximately March 21st to June 21st), this hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun, receiving more direct sunlight and experiencing warmer temperatures.
Solstices and Equinoxes
The solstices and equinoxes mark significant points in Earth’s orbit. The summer solstice is when a hemisphere receives the most direct sunlight, resulting in the longest day of the year. The winter solstice is the opposite, with the shortest day and least direct sunlight.
Conclusion
Earth’s 23.5-degree axial tilt is the fundamental reason for seasonal variations. This tilt influences the amount of solar radiation received by each hemisphere, leading to the distinct seasons we experience. Understanding this simple yet profound concept helps us appreciate the intricate workings of our planet.





